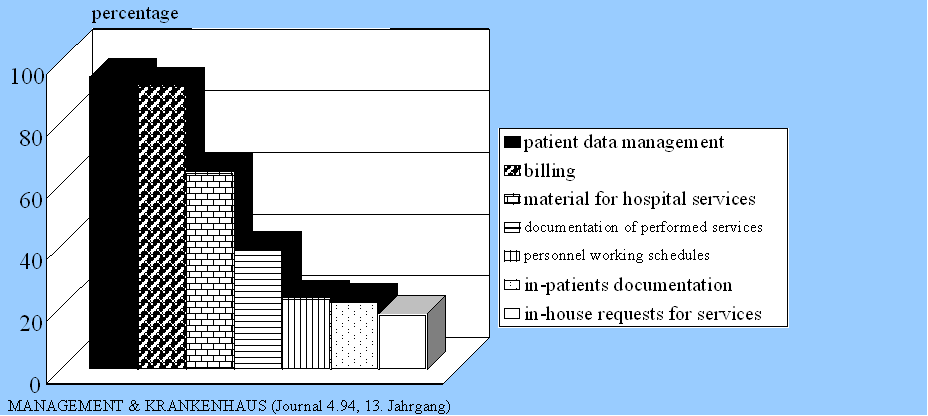
Figure 1: How are computers used in hospitals? [8] [4]
Telematic Tools Requirements for Statistical Data seen by Epidemiological and Health Economical Point of View
(Excerpts from a report at the Berlin G7 oncology meeting on Dec. 1st 1997)
O. Goldschmidt, H. Brunner, K. Lauterbach
University of Cologne (Germany)/ Institute for Health Economics, Medicine and Society
Summary:
At the moment general practitioners (GPs) and many hospitals are using old systems, platforms and software for their data and billing management. We can assume that there are (relatively) more patients using home computers and the WWW than practitioners. Concerning the WWW there is lack of a common structure, quality or any kind of co-operation regarding the different providers of internet services. There are a lot of new challenges getting the different telematic projects structured now. It is necessary to find a kind of platform of communication that have to be worked on in the next years. After some investigations in the new technologies there are great chances to reduce costs and improve quality in delivering health care. If the safety, data and economical requirements are considered from the early beginning, it should be possible to find promising solutions.
Status quo:
At the moment general practitioners (GPs) have old systems, platforms and software for their nursery management. Only 63% of 120,000 GPs were using computers in 1996 in Germany. We can assume that there are (relatively) more patients getting information from the WWW by home computers than practitioners. Furthermore - there is lack of a common structure, quality or any kind of co-operation regarding the different providers of internet services.
|
Figure 1: How are computers used in hospitals? [8] [4] |
|
It can easily be seen that the most important task of computer systems in a hospital is billing and patient data management for administrative processes.
|
Figure 2 gives an impression of what happens, when hospital managers, doctors and nurses are asked to rank given indicators or components of delivering health care to the patient. [1][6]
|
|
What is needed?
|
Figure 3 visualises the idea for a possible architecture when designing a common platform in medicine based on internet features. [3]
|
|
What are the challenges of a platform solution?
The challenge of shared databases between hospitals and GPs? [7]
Examples for cost-reducing challenges of telematic services: [2]
Finally some of the most important aspects of basic requirements - when talking about network solutions and integrating telematic tools into a kind of structured design - should be summarised:
Requirements for statistical data in telematic services are: [5]
Requirements from the health economical point of view:
Requirements for quality management purposes:
Besides these general requirements - fitting for many projects - there are some more interesting health economical analyses to do (to evaluate such a system, its acceptance and outcome).
As health economical tools:
can be used for evaluation.
Health economical analysis is based on:
There are a lot of challenges getting the different telematic projects structured. It is necessary to find a kind of platform of communication that have to be worked on in the next years. This article should encourage using telematic tools. After some investigations in the new technologies there are great chances to reduce costs and improve quality in delivering health care. There is no guarantee of having success. If the requirements are considered as shown above from the early beginning, then it should be possible finding promising solutions. Co-operation with other health care providers can help building a new standard of medical communication.
References:
|
[1] |
Caramés, J.; Rodriguez, P.; Diaz, L.: Defining quality of hospital Care - hospital managers survey. In: International Society for Quality Assurance in Health Care - The Quality of Health Services in a United Europe: Lessons for Others; Tenth International Conference on Quality Assurance in Health Care. Sonodruk, NL-Heino: 257 (1993) |
|
[2] |
Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V.: Telemedizin/Fern-Diagnose und –Betreuung von Risikopersonen und ambulanten Patienten. Presse- und Öffentlichkeitsarbeit Köln, Nr. 05/97-Ko: 1-11 (1997) |
|
[3] |
Goldschmidt, O.; Brunner, H., Lauterbach, K.W.: Anforderungen an ein valides Patienten- und Arztinformationssystem am Beispiel einer Evidenz-basierten Leitlinie zur Therapie der Adipositas auf Basis einer bewerteten Literaturdatenbank. Internal paper/proposal: 1-4 (1997) |
|
[4] |
Goldschmidt, O.J.: Qualitätssicherungsmaßnahmen im Bereich der Hals-Nasenohrenheilkunde. Berichte aus der Medizin, Shaker-Verlag Aachen (1997) |
|
[5] |
Hinzpeter, B.; Troche, C.J.; Pfeiffer, M.; Lauterbach, K.W.: Zur Bedeutung von Kosten-Nutzen-Analysen im Gesundheitswesen. Gesundh.ökon.Qual.manag. 2: 145-150 (1997) |
|
[6] |
Martinez, D.; Alonso, F.; Diaz, L.; Rodriguez, P.; Repullo, J.R.: Defining quality of hospital Care - doctor and nurse survey. In: International Society for Quality Assurance in Health Care - The Quality of Health Services in a United Europe: Lessons for Others; Tenth International Conference on Quality Assurance in Health Care. Sonodruk, NL-Heino: 305 (1993) |
|
[7] |
N.N.: Krankenhausintegrierende Versorgungsnetze – Bericht von der 92. Hauptversammlung des Marburger Bundes. mb-Ärztliche Nachrichten: 6 (1997) |
|
[8] |
The Boston Consulting Group GmbH & Partner: EDV wird nur in der Verwaltung eingesetzt. Krankenhaus und Management, Nr. 4 (13): 1 (1994) |